Article originally published through the AHLA 2025 Health Care Transactions Resource Guide on 4/25/2025.
Abstract
Healthcare continues to attract meaningful private investment, driven by opportunities for innovation, market consolidation, and improved patient care. However, investments are increasingly complex, with heightened regulatory scrutiny and evolving compliance requirements. By considering potential risks, this guide aims to provide practical approaches to healthcare transactions, from inspecting enterprises to effectively protecting capital investments. We examine the intricate balance between strategic priorities, due diligence, and government oversight—with a particular focus on valuation considerations.
Introduction
The healthcare industry remains attractive for investment capital, with investors deploying funds across an array of assets, from provider platforms and outpatient networks to digital health startups, diagnostics labs, and emerging biotech ventures. In fact, the primary plays of multisite clinics and payor contract negotiation have evolved into a more complex transactional panorama shaped by regulatory scrutiny, technological innovation, and escalating demand for clinical integration and patient-centric care.
This guide is written from the perspective of healthcare professionals who are involved in multiple aspects of such transactions. In our experience, the vantage points of each stakeholder in these arrangements—from investors to operators to valuators—offer unique insights for managing capital deployed in modern-day healthcare mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Whether structuring a majority investment in a behavioral health platform, acquiring a specialty surgical group, or underwriting a growth round for a genomics company, the stakes are high for every dollar contemplated.
For instance, as investors contemplate life sciences transactions, they often assess fundraising goals for early, mid, and late-stage opportunities. In doing so, they are fueling development-stage biotechs, data analytics companies, and contract research organizations. Conversely, commercial-stage deals demand careful assessment of clinical data, intellectual property (IP) value, and reimbursement strategy. In provider services—ranging from dermatology to cardiology, women’s health, and orthopedics—transactions increasingly target vertically integrated platforms that offer scalability and value-based care capabilities. This trend likely reflects a strategic shift towards enhancing operational capacity and geographic reach. Meanwhile, in the digital health space, transactions activity spans remote monitoring, artificial intelligence (AI)-based clinical decision support tools, and virtual care enablement—sectors where valuation narratives must balance user growth with evidence of clinical and financial return on investment.
This guide delivers a practical framework for safeguarding enterprise value across these types of transactions. To do so, we focus on five pillars of healthcare investment: clinical quality, operational strength, liquidity management, long-term strategic positioning, and regulatory compliance. We first examine how each contributes to valuation and capital protection and then explore the mechanics of comprehensive due diligence, disciplined risk management, and proactive regulatory oversight—each of which is indispensable to steering today’s healthcare investment environment.
From leading a platform roll-up, evaluating bolt-on acquisitions, to performing diligence on a life sciences target, the goal is the same: to deploy capital intelligently, protect it rigorously, and grow it sustainably. This user guide delivers important constructs for consideration.
I. Strategic Priorities for Healthcare Investments
1. Prioritize Patient Care and Clinical Excellence
Aligning investment strategies with clinical excellence and superior patient care is central in mitigating regulatory risks and enhancing market position. Strategic investments in modern tech and evidence-based processes are key to achieving these objectives.
- Technology in Healthcare: Healthcare groups are increasingly adopting cutting-edge technologies to improve clinical outcomes. For example, the integration of AI-driven diagnostic tools and surgical robotics has been shown to enhance procedural accuracy, helping surgeons make decisions during operations.[1] Companies also develop AI agents capable of automating administrative tasks and assisting in patient care, aiming to reduce provider burnout and improve overall care quality.[2]
- Clinical Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Teams that measure comprehensive clinical excellence metrics and implement performance-monitoring systems ensure that investments translate into measurable improvements in patient care. These systems can track a wide array of indicators, from clinical and treatment efficacy to patient-reported outcomes and long-term health status. By rigorously analyzing performance measures, organizations identify areas for clinical gains and demonstrate best-case scenarios of their investments to patients and stakeholders.
- Patient Outcomes: Safeguarding financial impact connects closely with clinical excellence—and optimal patient outcomes reflect this priority. Therefore, incorporating novel viewpoints to develop innovative provider compensation models has become indispensable. These types of models reward activities including quality outcomes, upstream contributions to clinical research, adoption of best practices, and leadership in medical advancements. Similarly, the implementation of advanced risk-stratified care models that incentivize personalized, evidence-based treatments and long-term patient health management further supports this alignment.
Valuation Perspective: Organizations that demonstrate commitment to clinical excellence often carry higher market valuations. The enhancement stems from a team’s ability to deliver superior patient outcomes which, in turn, not only improves reputation but also attracts more patients and payors. Similarly, investments in technology, personnel, and business models that improve patient experiences can notably increase an organization’s value. Moreover, aligning value analysis with clinical excellence optimizes resource utilization and ensures the sustainability of healthcare delivery, further boosting an organization’s market standing.[3]
2. Operational Strength
Operational strength not only serves as a primary line of defense in protecting capital investments in healthcare but also provides a roadmap to accretive investment. Value-driven leaders incorporate efficient processes, resource allocation, and alignment to market conditions. Optimizing operations to enhance the quality of patient care resonates with financial sustainability.
- Operational KPIs: Many successful management teams implement robust operational metrics and KPIs to monitor and improve operational strength. Relevant indicators include patient throughput, resource utilization rates, and cost per episode of care. Regular review of these metrics can help organizations identify performance gaps.
- Automation: Organizational investment in technology and automation can further boost operational strength. Examples include the implementation of smart scheduling platforms, automation of billing processes, and use of AI to aid operational decision-making. Many effectual teams rely on these technologies to reduce errors and enhance quality assurance.
Valuation Perspective: Strong operational performance is a key driver of value. Valuators examine operational metrics, efficiency ratios, and productivity measures when assessing the value of a healthcare organization. Organizational management that shows superior operations—marked by smart capacity planning, technology-driven process improvements, and agile resource allocation—command higher valuations due to management’s ability to generate stronger cash flows and adapt to market changes more effectively.
3. Liquidity Management
A healthy operation will maintain adequate liquidity at the clinic level for steering day-to-day operational challenges and ensuring uninterrupted patient care. In fact, many effective financial controllers consider implementing multi-tiered cash management systems which are tailored to specific needs (e.g., daily operating, reserve, strategic, and debt covenant considerations).
- Leading Indicators: An effective financial manager regularly monitors and adjusts clinic-level liquidity based on patient volume and reimbursement cycles. Leading indicators to consider include seasonal and geographical fluctuations in patient visits and payor mix that could shape revenue streams and cash flow at the clinic level.
Valuation Perspective: Effective clinic-level liquidity management can alter an organization’s operational efficiency and financial resilience. Valuation professionals assess the clinic’s cash management practices, including its ability to meet day-to-day operational costs and adapt to short-term financial challenges. In fact, organizations demonstrating strong liquidity management at the local level may contribute to lower operational risk assessments in valuation calculations—a circumstance that can potentially enhance the overall valuation of the healthcare organization.
4. Value Creation Based on Long-Term Trends
Focusing on sustainable growth strategies is essential for protecting and growing capital investments in healthcare. For instance, a current focus incorporates investment in technologies and innovations that address long-term healthcare challenges. Such investments include digital health platforms, AI-driven diagnostic tools, and advanced data informatics that can improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency over time.[4]
- Evolving Business Models: Creating scalable models that can adapt to changing operating environments is central for long-term success. The operating model should have sufficient flexibility to accommodate reimbursement trends and care delivery models. Institutional leadership and receptivity can help to protect investments from disruptions and market shifts. In fact, health systems that invest in AI and digital transformations appear better positioned to traverse changes effectively.[5]
- Macro Trends: Focusing on investments in areas with strong demographic trends and unmet medical needs can provide a solid foundation for long-term value creation. By example, positive results may occur by focusing on issues such as services for aging populations, chronic disease management, or solutions for underserved communities. By aligning investments with these long-term trends—such as the expected doubling of the 60+ population by 2050 and the corresponding rise in demand for senior care and chronic disease services—organizations can position themselves for sustained growth and impact.[6]
Valuation Perspective: Strategies focused on long-term value creation can augment an organization’s perceived value. In fact, when forming valuation opinions, appraisers assess numerous factors including strategic initiatives, technological investments, and market positioning. Organizations that demonstrate a clearer path to long-term value creation benefit from more optimistic future cash flow projections and potentially lower risk premiums in valuation calculations. Further, platforms that embed value-based healthcare principles into their operating models—such as the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) and commercial accountable care organizations, ACO REACH, Medicare Advantage plans, commercial shared savings arrangements, and direct to employer risk arrangements—tend to align more effectively with improving patient outcomes. Doing so allows organizations to enhance the health of a population while reducing unnecessary waste and uncoordinated care. These results ultimately create scalable impact and resonate with private equity and strategic acquirers seeking long-term value creation.
5. Focus on Compliance
Strong compliance programs are often invisible when well-functioning as they support smooth, uninterrupted operations across the organization. On the other hand, when compliance goes wrong, stakeholders quickly feel the consequences. The compliance team plays a decisive role in developing a robust framework for protecting investments and ensuring long-term success. Their process should begin with establishing direct access to leadership, bypassing agency or committee. The team should be empowered to develop, implement, and oversee comprehensive compliance programs that address all relevant regulatory requirements. Programs that do so ensure that organizations adhere to laws, regulations, and ethical standards—thereby protecting the quality of care, mitigating risk, and maintaining stability.
- Monitor Changes: An enterprise should regularly update compliance programs to address new regulations and industry best practices. Such programs require ongoing diligence activities such as (i) monitoring regulatory changes at both the federal and state levels, (ii) staying abreast of enforcement trends and industry standards, and (iii) maintaining a dynamic environment, with built-in mechanisms for regular review and updates.
- Culture: Fostering a culture of compliance throughout the organization is perhaps the most salient aspect of an effective compliance strategy. Culture involves more than just implementing policies and procedures; it entails creating a unit wherein every employee understands the importance of compliance and feels empowered to raise concerns. Regular training as well as clear communication and feedback channels are key components of building such a culture.
Valuation Perspective: A robust compliance framework can influence an organization’s value. Investors and potential buyers often place a premium on healthcare entities with reliable compliance records and systems, given their importance in reducing regulatory risks and potential liabilities.[7] In assessing the value of a healthcare organization, appraisers determine the strength and effectiveness of compliance programs by considering factors such as the comprehensiveness of policies, the frequency of audits, and the organization’s history of regulatory compliance.
II. Due Diligence/Risk Management
1. Comprehensive Due Diligence
Thorough due diligence is indispensable for identifying and mitigating risks in healthcare transactions. Overlooking critical compliance or operational issues during a deal can derail the transaction or lead to costly legal battles. As such, investors must approach this process with deliberate tact. While not an exhaustive list, the following matters are topical examples of diligence checklist considerations:
- Regulatory: In assessing the regulatory landscape specific to the company’s operations, the team must understand not just current regulations but also pending legislation and regulatory trends that could modify the company’s future operations.
- Finance: A comprehensive financial health evaluation should delve beyond surface-level financial statements to uncover the true economic condition of the target. Specifically, a popular evaluation is the Quality of Earnings (QoE) analysis, which scrutinizes the sustainability and reliability of revenue and profit streams. By dissecting revenue sources, expense structures, and potential liabilities, stakeholders can gain a clear picture of the organization’s financial stability and future performance prospects. Such detailed measurements are vital for identifying risks and opportunities, thereby informing negotiation strategies and decision-making processes.
- Case/Payor Mix: Understanding the variety of services provided and the distribution of revenue across different payors offers insights into revenue predictability and potential reimbursement challenges. For instance, a healthcare provider heavily reliant on Medicaid may face more reimbursement variability as compared to one with a predominantly private insurance payor mix. This knowledge aids in forecasting future revenue trends and assessing the outcome of changes in payor contracts.
- Reimbursement Rate Trends: By examining historical reimbursement rates and payor contract terms, acquirers gauge the sustainability of revenue streams. For example, if a provider has been operating under outdated insurance contracts, due diligence might reveal opportunities for renegotiation that could lead to higher levels of reimbursement. Detailing the information showing trends (often precipitated by changes to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS))—versus simply a current snapshot—is important in this exercise.
- Contracts: The diligence team must review existing contracts—particularly those with providers and vendors—to understand potential risks and obligations. The review should assess not only the financial terms of these contracts but also any compliance-related provisions, performance metrics, and termination clauses that may affect the company’s operations or value.
- Cybersecurity: In the digital age, cybersecurity has emerged as a paramount concern in healthcare M&A. The integration of technology systems in M&A can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities, making the combined entity susceptible to cyber threats. In 2024, for healthcare providers alone, 181 confirmed ransomware attacks compromised 25.6 million health records, with significant economic damage.[8] Therefore, conducting thorough cybersecurity due diligence must be paramount and non-negotiable.[9]
Valuation Perspective: Comprehensive due diligence is necessary in accurately assessing a healthcare organization’s value. Valuation professionals will closely study the strength and effectiveness of target programs as they relate to compliance, financial health, case/payor mix, and cybersecurity. For example, inadequate cybersecurity measures may lead to financial losses and reputational damage, negatively impacting said valuation.
2. Risk Management
An organized process to identify and prioritize risks is key for effective risk management in transactions. A proactive solution includes implementing a risk management matrix to classify and rank potential threats.[10] The matrix should consider factors that include the likelihood of a risk occurring, its potential effects on the organization, and the difficulty or cost of mitigating the risk.[11]
Below is an abbreviated example:
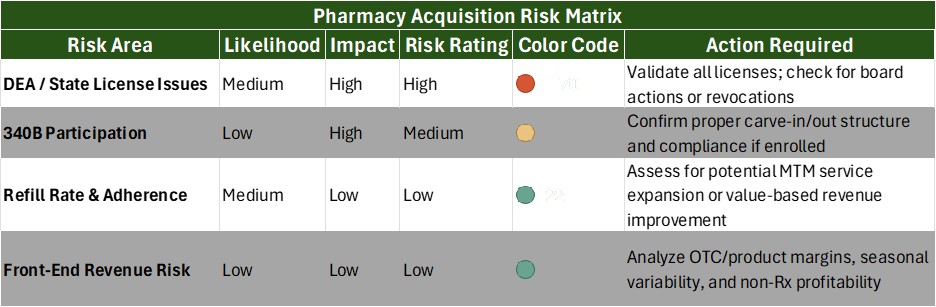
In addition to developing this type of tool, leaders should engage in the following activities to mitigate risk on an ongoing basis:
- Periodic Review: The impact of regularly reviewing and updating risk assessments is often underestimated. Risk management should be an ongoing process, with formal reviews conducted at least annually. More frequent reviews may be necessary in response to regulatory backdrop, operational modification, or previously identified deficiencies.
- Holistic Collaboration: Engaging cross-functional teams in the risk identification process provides a comprehensive view of potential threats. A collaborative approach brings together expertise from various areas of the organization, including:
- Clinical perspectives,
- Financial insights,
- Legal considerations, and
- Operational viewpoints.
Integrating these diverse perspectives leads to more thorough risk appraisals and insightful recommendations. Ultimately, this type of collaborative approach ensures an all-inclusive risk overview which enhances organizations’ ability to develop effective risk mitigation strategies.
Valuation Perspective: The quality and completeness of risk evaluation processes can shape its perceived value. Valuation professionals gauge the robustness of these processes as part of their analysis. Companies with modern, sophisticated risk management systems may be viewed as lower risk investments, potentially justifying higher valuations.[12] These organizations are often seen as better equipped to anticipate and manage uncertainties. Additionally, the identified risks and their potential concerns will be factored into valuation models, influencing projections and risk-adjusted discount rates. The comprehensive approach to risk management not only protects the organization but also enhances its value proposition to the market.
III. Navigating Government Oversight
1. Staying Current on Regulatory Changes/Case Law
Forward-looking teams implement proactive monitoring systems to stay informed of regulatory changes and case law developments. Always-on systems should include subscriptions to regulatory alert mechanisms, routine web checks of government agencies, and strong relationships with industry associations that provide regulatory insights.
New entrants to healthcare, including tourist investors, receive no leniency from the Office of Inspector General (OIG) when it comes to understanding the applicable regulatory framework. The OIG emphasizes, “New entrants should take steps to ensure that they and any business partners possess a solid understanding of the Federal fraud and abuse laws, in addition to other applicable laws, and that they possess an understanding of the critical role an effective compliance program plays in preventing, detecting, and addressing potential violations.”[13]
- Staying Informed: Engaging with industry associations and legal counsel are important actions to ensure understanding of the practical implications of regulatory changes. Regular check-ins provide valuable context and analysis beyond the regulatory updates themselves, signaling precursors to enforcement methods and necessary compliance steps. In fact, some organizations have turned to offshore compliance functions and Regtech tools, aiming for budget-friendly compliance.[14]
Valuation Perspective: A team’s ability to stay informed of and adapt to regulatory changes can influence its perceived value. Valuation professionals assess an organization’s regulatory intelligence capabilities as well as its track record of adapting to regulatory shifts. Organizations that demonstrate agility and foresight in navigating regulatory changes may be viewed as lower risk investments, potentially justifying higher valuations.
2. Preparing for Regulatory Scrutiny/Inquiries
Fully prepared healthcare organizations remain ready to effectively respond to regulatory inquiries or investigations, with an aim to protect investments and maintain operational continuity. Preparation begins with developing and maintaining comprehensive documentation of compliance efforts, covering all aspects of the compliance program including policies and procedures, training materials, audit results, and records detailing how compliance issues have been addressed.[15]
- Preparation: Establishing clear protocols for responding to regulatory requests is crucial for ensuring a timely and appropriate response. These protocols should outline the steps to be taken when a regulatory inquiry is received, including notification procedures, processes for information gathering and review, and response formulation and approval methods.
- Readiness: Conducting regular internal audits helps organizations proactively identify and address potential issues, staying ahead of regulatory concerns. Audits should cover all areas of the organization’s operations, with a particular focus on high-risk areas identified through the risk calculation process.
Valuation Perspective: Valuation professionals assess the robustness of a team’s documentation practices, response protocols, and internal audit processes. Organizations demonstrating a high level of preparedness for regulatory inquiries may be viewed as lower risk investments, potentially leading to more favorable valuations. Additionally, a history of successfully overseeing regulatory inquiries is generally viewed as a positive factor, showcasing the organization’s resilience and capacity to mitigate future risks, which is often seen as a strong indicator of long-term stability and trustworthiness in the marketplace.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
- Diligence must be deep and multi-dimensional. Scrutinize clinical quality, review payor mix/contracts, reimbursement rates, cost structure, cyber posture, and contract dependencies.
- Operational performance drives value. Track KPIs; plan efficient workflows, resource allocation, and automation to improve throughput and financial sustainability.
- Stay ahead of technology shifts. Incorporate emerging tech—AI tools, intelligent scheduling, and automated billing.
- Integrated risk management supports higher multiples. Identify, prioritize, and mitigate risk across financial, operational, clinical, and legal domains.
Protecting capital investments in healthcare transactions requires an approach that weighs multiple priorities. The viewpoints outlined in this guide provide an attuned framework for advancing healthcare investments that considers financial, regulatory, and clinical facets. By building strategic systems, quality-first care mindsets, operational and financial merit, and staying ahead of compliance trends, investors and operators can ensure enduring enterprise value. Participants who adapt to increased scrutiny while pioneering delivery models and advancing care quality will be best positioned for long-term success. These mindsets bridge organizations toward creating sustainable value while contributing to the improvement of healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
As healthcare investments continue to evolve, it is imperative for leaders to continuously reassess their strategies and priorities in light of new regulations, market dynamics, and technological advancements to protect investment capital.